Omega-3 Fatty Acids

What are Omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are an essential nutrient that our body needs to function. However, because the latter cannot be produced by the body, the solution is to ensure that you incorporate omega-3-rich food in your diet or take fish oil supplements. Whichever choice you make, it is vital that you understand how your body processes different forms of omega-3 and how you can choose the best source.

Omega-3 comes in multiple forms and sources. The three primary types of omega-3 are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentanoic acid (EPA):
- ALA is found in many plant foods, including kale, spinach, soybeans and many seeds and nuts such as chia, flax, hemp, walnuts and almonds. ALA has to be converted into EPA or DHA before it can be utilised by the human body.

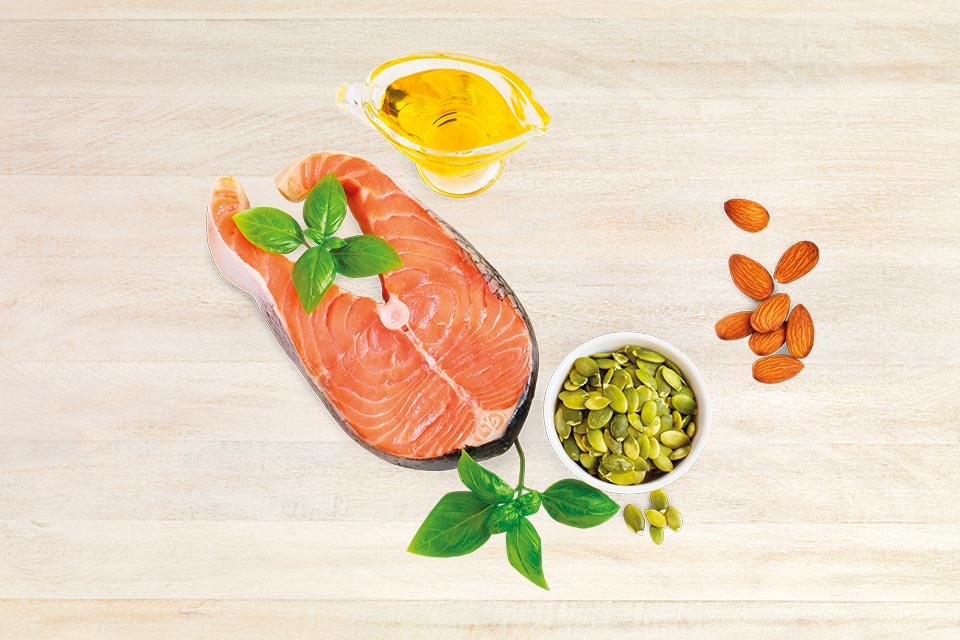
- EPA and DHA can be found in fatty fish like salmon, trout, mackerel, anchovies and sardines that feed on microalgae. If you do not eat a lot of these foods, then omega-3 supplements can be useful.

Are You Getting Enough Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
A study conducted in Malaysia found that the dietary levels of omega-3 fatty acids among its participants were very low. According to the study, the level of omega-3 fatty acids of its participants were reported to be in the region of 0.22-0.28% kcal, which is below the Malaysian recommended range of 0.30-1.20% kcal.
WHY OMEGA-3?
Rich in anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3 contribute to important health benefits such as: